Pain
What Are Hereditary Neuropathies?

What is Hereditary Neuropathy?
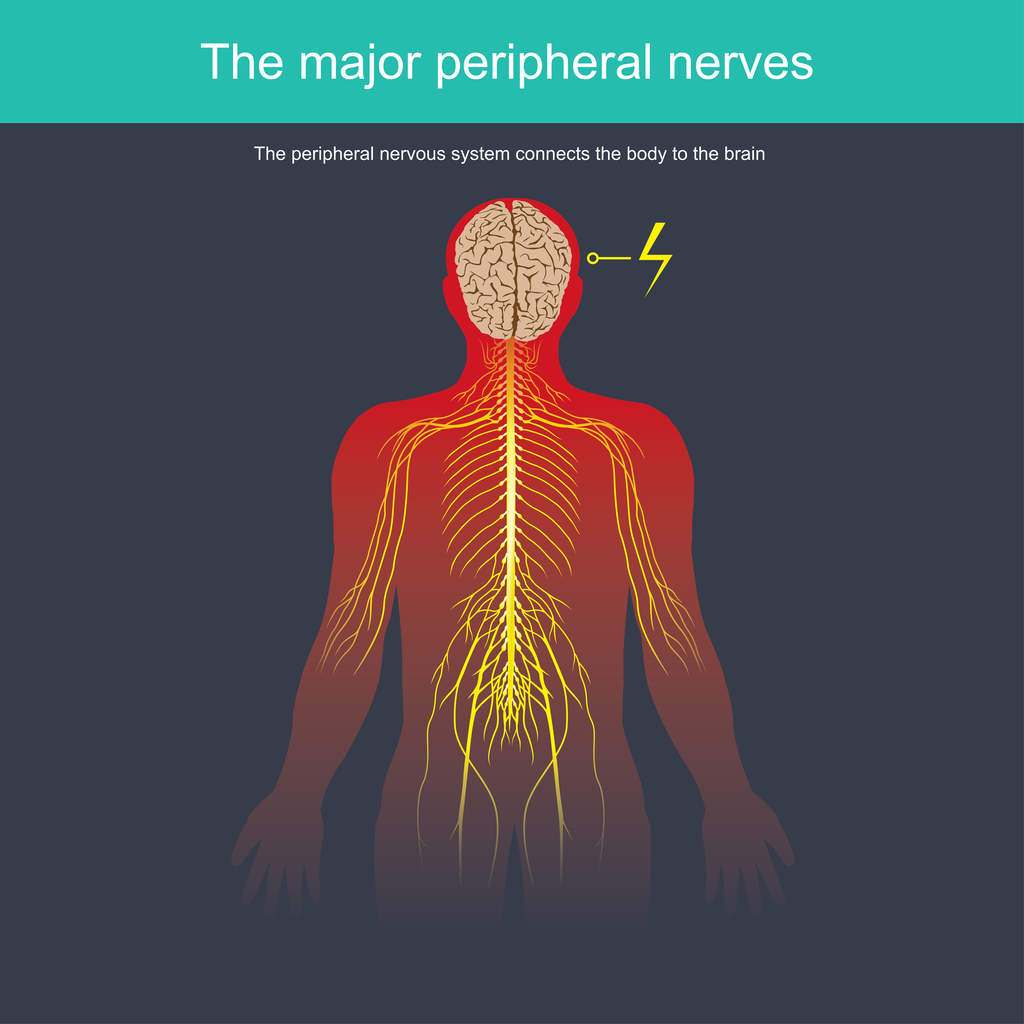
Peripheral neuropathy is a medical condition that develops when the peripheral nerves are damaged. The peripheral nervous system is the communication network connecting the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord) to every other body part. Symptoms vary depending on the cause and the specific nerves affected. Hereditary neuropathies are a type of nerve pain that is genetically inherited from parent to child.
Hereditary neuropathies are grouped into four main subclasses.
- Hereditary Motor Neuropathy
These neuropathies involve damage to the nerves that communicate with consciously controlled muscles, such as those used to walk and talk. One example is spinal muscular atrophy distal type V. - Hereditary Sensory neuropathy
These neuropathies involve damage to the sensory nerves which connect to the skin. Sensations, such as temperature, touch, and pain, are affected. For example, hereditary sensory neuropathy type IA - Hereditary Sensory Autonomic Neuropathy These neuropathies combine sensory neuropathy, which affects how sensations are experienced, such as temperature, touch, or pain, with automatic neuropathy, which involves damage to the nerves that communicate with organs and muscles that are not consciously controlled, such as the heart and digestive system — for example, Riley-Day syndrome.
- Hereditary Sensory Motor Neuropathy
These neuropathies involve damage to the sensory and motor nerves. This affects how sensations are experienced, such as temperature, touch, and pain, as well as how nerves communicate muscles that are consciously controlled. Examples include Peroneal muscular atrophy and Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease.
Symptoms
The symptoms that could be experienced for each neuropathy depend on the type of nerves it affects.
Sensory neuropathy symptoms can include:
- Tingling, pins, and needles
- Numbness, inability to feel pain or temperature
- Cuts or sores that are slow to heal
- Sharp, jabbing, throbbing, or burning pain
Autonomic neuropathy symptoms can include:
- Too much or too little sweating
- Postural hypotension or low blood pressure
- Insensitivity to pain
- Heat intolerance
Motor neuropathy symptoms could include:
- Weakness
- Loss of muscle mass
- Lack of coordination or balance
- Difficulty walking
Other symptoms associated with hereditary neuropathies include:
- Foot deformities such as high foot arches or hammer toes
- Thin calf muscles
- Scoliosis
Cause
Hereditary neuropathies are caused by a child inheriting a gene from a parent. The exact inheritance pattern and gene may be known, depending on the specific condition.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for hereditary neuropathies include:
- Having a parent or grandparent with a hereditary neuropathy
- Having a sibling with a hereditary neuropathy
- A past family history of hereditary neuropathy
Additional Sources Science Direct and Advocate Health Care