Pain
Treatment Options for Serious Back Pain
Source: WebMD, National Center for Biotechnology Information: U.S. National Library of Medicine: National Institutes of Health, Johns Hopkins Medicine, Cleveland Clinic
261 people found this helpful
Print
Share
Save
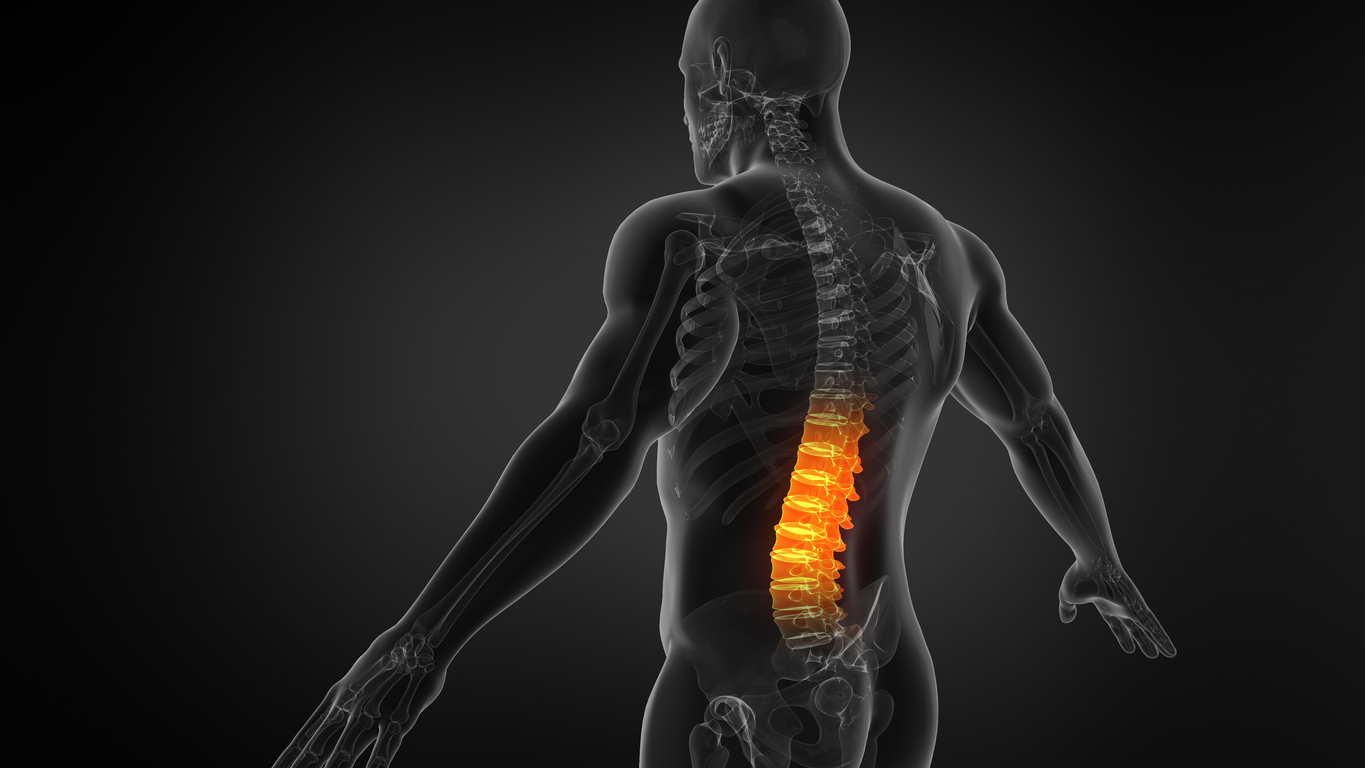
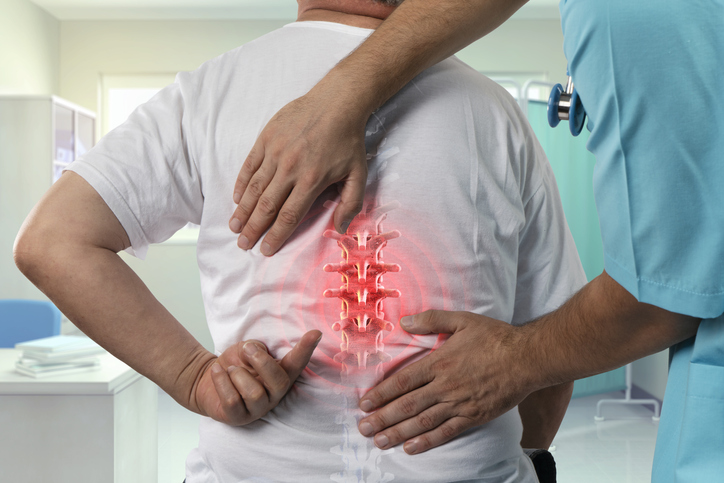
An estimated eight out of every ten people will experience back pain at some point in their lives. Back pain is one of the most common reasons people visit a physician. It can be caused by normal wear and tear, overuse, injuries, muscles, bones, nerves, or discs. The most common causes of back pain are muscular irritation and joint dysfunction.
Treatment options for serious back pain
A health care professional will recommend proper treatment after diagnosing the cause of back pain. Various diagnostic tests can help determine the cause. Treatment options include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as over-the-counter ibuprofen or naproxen, can reduce pain symptoms and stiffness. If symptoms are severe, a stronger NSAID may be prescribed, such as indomethacin, diclofenac or celecoxib. Although NSAIDs may reduce inflammation, pain and stiffness, they may also cause gastrointestinal bleeding. A health care provider should be consulted regarding NSAID dosage to prevent complications.
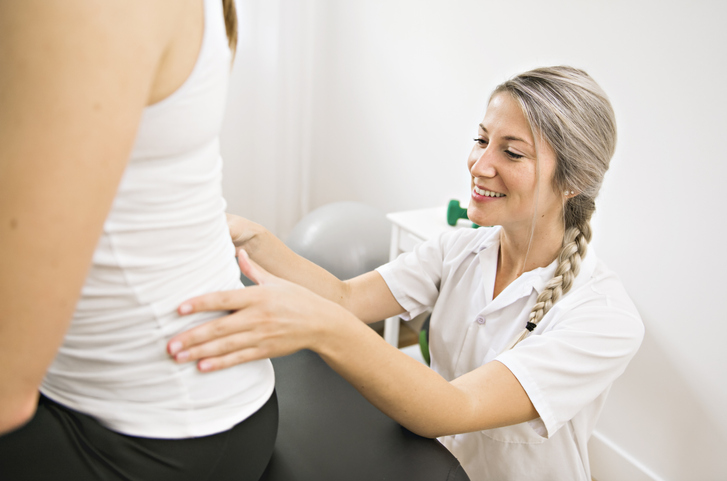
- Chiropractic care focuses on controlled force to a spinal joint. A trained specialist (chiropractor) aligns the musculoskeletal structure (especially the spine) through hands-on manipulation, which improves physical function and spinal motion. It can also reduce pain symptoms, including inflammation and muscle tension.
- Transcutaneous electric nerve stimulation (TENS) is a non-invasive pain-reduction therapy that involves using a portable device (TENS unit) that applies slight electrical pulses on painful areas of the body. These electrical pulses flood the nervous system, reducing its ability to transmit pain signals from the spinal cord to the brain. The electrical pulses also cause the body to produce natural pain relievers called endorphins.
- Bioelectric therapy is a safe form of treatment used for chronic pain and acute pain conditions. Bioelectric currents intercept and block pain messages from reaching the brain. It involves electrodes being applied to the skin at the affected areas. It may also entail rubber suction cups. A computer program controls the electric stimulation.
- Nerve blocks are medical procedures that block specific nerves from sending pain impulses to the central nervous system (CNS). They are categorized in several ways: why they are done (therapeutic, diagnostic, prognostic or preemptive), how they are done (non-surgical or surgical), and where they are done on the body (neck, back, etc.).
- A spinal cord stimulator (SCS) is a small-implanted device that sends electrical pulses to mask pain signals from reaching the brain. It can help reduce chronic pain and opioid usage. The effectiveness of spinal cord stimulation will vary from individual to individual, which is why a trial stimulator is used prior to permanent implantation.
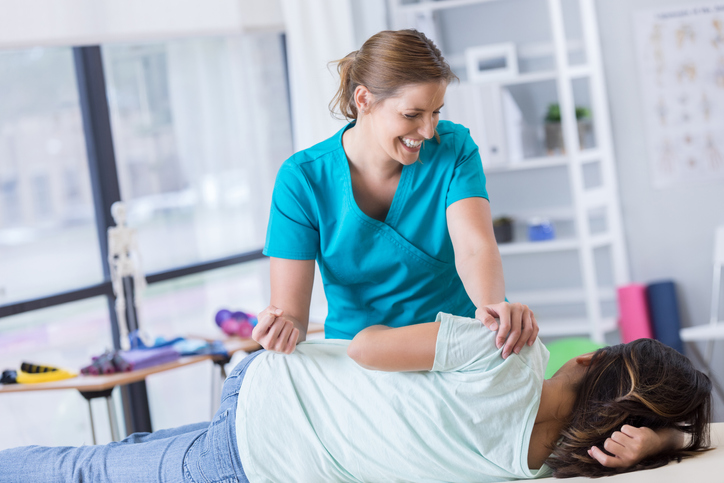
- Physical therapy is often used as a standard treatment for chronic pain or pain related to an injury; however, it can also help treat other medical conditions, including back pain. A physical therapist treats areas of weakness by encouraging movement.
- Biofeedback is a technique in which an individual can learn to control specific bodily functions, such as heart rate, breathing, muscle contractions, and brainwaves. It can help an individual learn to relax muscles or reduce pain. Biofeedback can be ideal for individuals who are looking for a noninvasive, medication-free treatment.
- Back surgery is typically a last option to treat back pain. However, if conservative treatments fail to reduce chronic pain, surgery may be needed to decompress a nerve root, enlarge the spinal canal (laminectomy), stabilize segment(s) of the vertebra (fusion), or reduce a deformity (scoliosis). A laminectomy is the most common type of back surgery. It involves removal of the roof of one or more vertebrae. This creates additional space for nerves.